Intrusion Detection / Intrusion Protection Systems
Enhances Security and Saves Money
A major component of a highly secure architecture design is Intrusion Detection/Intrusion Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS). Businesses that have valuable assets to protect, compliance regulations to adhere to and that would be greatly affected by data breaches should include IDS/IPS throughout their architectural designs. The impact of cyberattacks on a business is undisputedly losses in finance, reputation, and legality. Businesses need to maintain a winning strategy and IDS/IPS enhances IT Security and saves money for businesses.
How does IDS/IPS work?
Working concurrently, IDS and IPS systems are designed to mitigate a vast array of attacks including viruses, worms, Trojans, Ddos, bots and phishing. IDS/IPS can stop attackers while they are gathering information about a network and produce logs that can be used for analytics and auditing. IDS and IPS systems are located inside a network and serve as additional security measures behind firewalls.
As traffic is traversing throughout a network, IDS/IPS can be configured to use a variety of approaches to monitor and protect a network:
Signature based approach: IDS/IPS compare network packets to the signatures of cyberattacks which are located within a cyberthreat database.
Anomaly based approach: IDS/IPS monitors abnormal and usual behavior, much like a credit card company monitors user transactions.
Policy based approach: IDS/IPS assesses security policy violations against the security policy predetermined by organizations.
Let’s take a closer look at following components: Cyberthreat Database, IDS and IPS.
Cyberthreat Database
This component is a database of attack signatures that is included in IDS/IPS products. An attack signature is a file containing a data sequence used to identify an attack on the network. These signatures take many forms of unauthorized access and suspicious network privilege use. Typically these databases are updated frequently, every 4-6 hours.
Intrusion Detection System (IDS)
This component is MONITORING quite like a Secret Service Agent for the President who is incessantly monitoring and analyzing the surroundings for anything suspicious. By comparing network packets to the cyberthreat database, an IDS can recognize threats and violations. However, just like a Secret Service Agent that doesn’t leave the President when danger is detected, an IDS is only sends notification of a threat. IDS is a reactive security system that does not combat threats. A system or person must look at the notifications that IDS generates, and threats must be combated by other components.
Intrusion Prevention System (IPS)
This component is PROTECTING quite like a police officer who is patrolling, sees a crime unfolding and takes action to stop the crime. Like an IDS, IPS compares network packets to the cyberthreat database and sends notification of the threat. However, IPS has the capability of combating threats. IPS will take action to permit or deny the network packet access to a target based on security rules. IPS prevents attacks by dropping packets, blocking offending IPs, closing access points, reconfiguring firewalls and alerting security personnel to potential threats. IPS is a proactive security system that can preemptively block attacks including remote file inclusions that facilitate malware injections and SQL injections used to access databases.
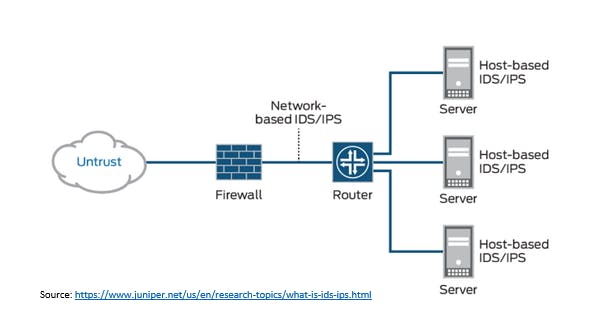
IDS/IPS in Architecture Designs
The most secured architectures are ones in which every layer and component is locked down and security is redundantly present. Therefore, it is advantageous to use IDS/IPS throughout a highly secure design. IDS/IPS can implemented strategically within a network, on servers and many Next Generation Firewalls already have IDS/IPS capabilities built into them.
IDS/IPS Criteria
There are many IDS/IPS available from manufacturers such as Palo Alto, Juniper, Cisco and Check Point. According to Network Security Software, to qualify for inclusion in the IDS/IPS category a product must meet the following criteria:
• Monitor IT systems for abnormal behavior and misuse
• Inform administrators of abnormal protocol activity
• Monitor the performance of IT hardware and security components
• Provide blocking mechanism for web-based threats
Written by Kenya Carl 5/19/22 Revised 5/23/22
References:
home.sophos.com/en-us/security-news/2020/wh..